ChatGPT, the AI chatbot model released by OpenAI, seems to be a game-changer for the AI industry and business in general.
While the majority of chatbots we were used to dealing with are primitive, ChatGPT opened a new era by showing that AI technology can carry on a conversation with multiple queries, generate software code, and fix programming prompts.
The use cases and advantages for everyone will be many. Yet, we need to consider also the challenges and risks that may arise around privacy and data security, particularly within the scope of GDPR.
We have tried ChatGPT and analysed the main privacy challenges that companies based in the EU may face.
What is ChatGPT?
ChatGPT is a variant of the already popular OpenAI’s GPT-3.5 language-generation software that has been designed to carry conversations with people. Some of its features include answering follow-up questions, challenging incorrect premises, rejecting inappropriate queries, and even admitting its mistakes.
And, in a not-so-far future, it may replace our beloved Lorem Ipsum.

For the sake of our brief analysis, we need to separate ChatGPT, the AI model, from OpenAI, the company behind it.
OpenAI is the company providing the ChatGPT services, and with regards to any personal data shared with the model, they are the Data Processors, and their servers and employees seem to be mostly in the United States.
What are the biggest privacy risks for companies looking to leverage this technology?
Although the tool can boost AI innovation, it is crucial to keep in mind that there are still some “grey areas” on the data protection and privacy side. We will focus our assessment on the GDPR.
The basic facts at this point are:
- OpenAI, the company developing ChatGPT, is a Data Processor and can process data coming from conversations.
- The company, its employees and servers are located in the US
- The data is the model receives is not used only for the provision of the service itself, but also for the improvement of the model outputs
This implies major challenges compliance-wise:
- Implementation of required measures to have OpenAI as a Data Processor
- OpenAI as a US Service Provider
- Implications of human labelling and training
OpenAI as your data processor
About the processing of data, Open AI states that:
[...] If your use of the Services involves processing of personal data, you must provide legally adequate privacy notices and obtain necessary consents for the processing of such data, and you represent to us that you are processing such data in accordance with applicable law.
So, if you are planning on sharing personal (or sensitive data) and you are under the scope of GDPR, you should contact OpenAI’s support to get the Data Processing Addendum in place. It is suggested to contact [email protected] to execute a Data Processing Addendum. Also, here is the link to OpenAI’s privacy policy in case you are curious: https://openai.com/privacy/
(In the current training version, you will find a disclaimer against sending sensitive data, as you sign up for the service).
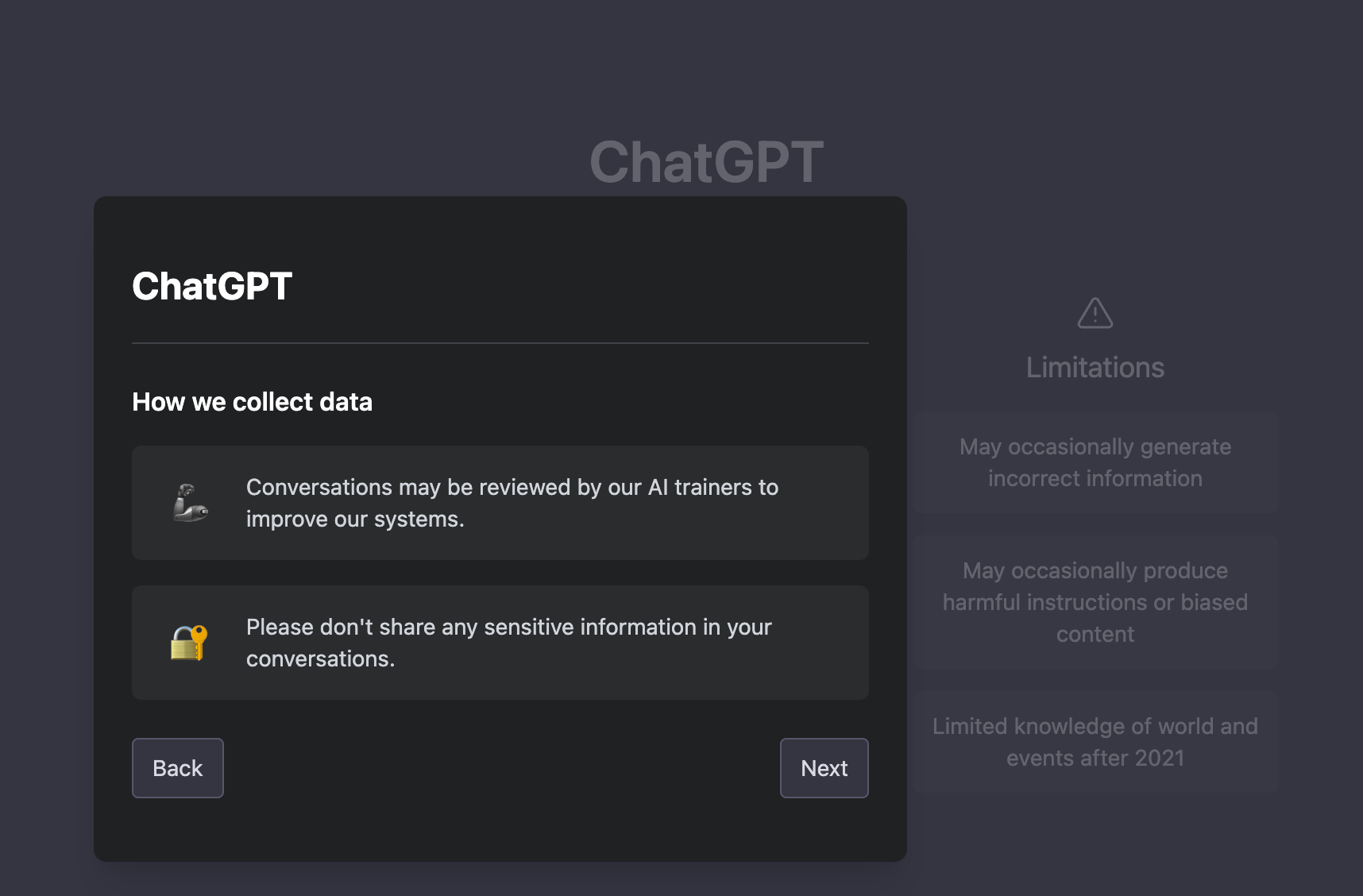
Even if you do not plan on sharing personal data explicitly with OpenAI, you should do this anyway, as OpenAI mentions in their policies that they may process IP addresses and other personal data associated with you.
Furthermore, if your use of ChatGPT involves the processing of personal data, you must provide legally adequate privacy notices to your users and obtain the necessary consents to process that data.
And last but not least, there are important considerations one must make in terms of how the tool is implemented in your own workflows and businesses, since you may easily fall within the cases considered by the GDPR as Profiling and Fully Automated Decision Making, which would require legal justifications from the controllers.
Just to feed our curiosity, we asked ChatGPT about users’ data. This is the reply we got:
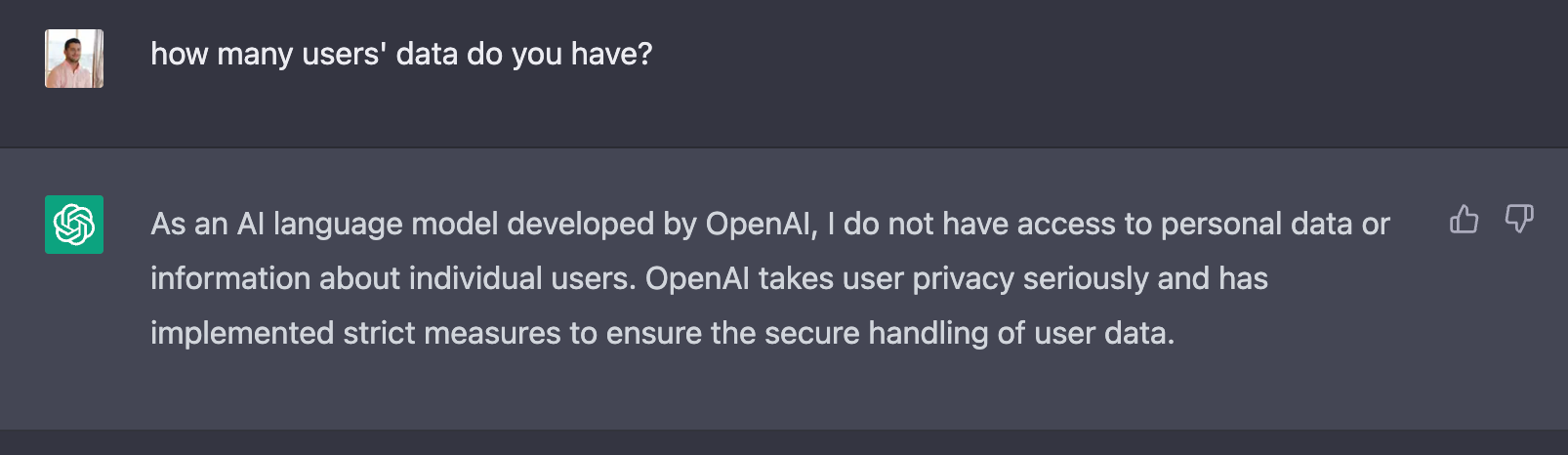
But, this is not entirely correct, as in the first screen, we can read that conversations can be reviewed by OpenAI’s AI trainers to improve their system. And there are also the disclaimers in their privacy policy.
The fact that sharing personal data is inherent to the use of the platform makes the next topic much more complex.
OpenAI as a US Service Provider
OpenAI is a US legal entity, and as far as we can tell from its Privacy Policy, its servers are in the US as well.
Currently OpenAI’s privacy policy states: “By using our Service, you understand and acknowledge that your Personal Information will be transferred from your location to our facilities and servers in the United States.”
Companies that are used to dealing with US service providers already know the complexities this implies from a GDPR point of view. Check out our blog article about the Privacy Shield.
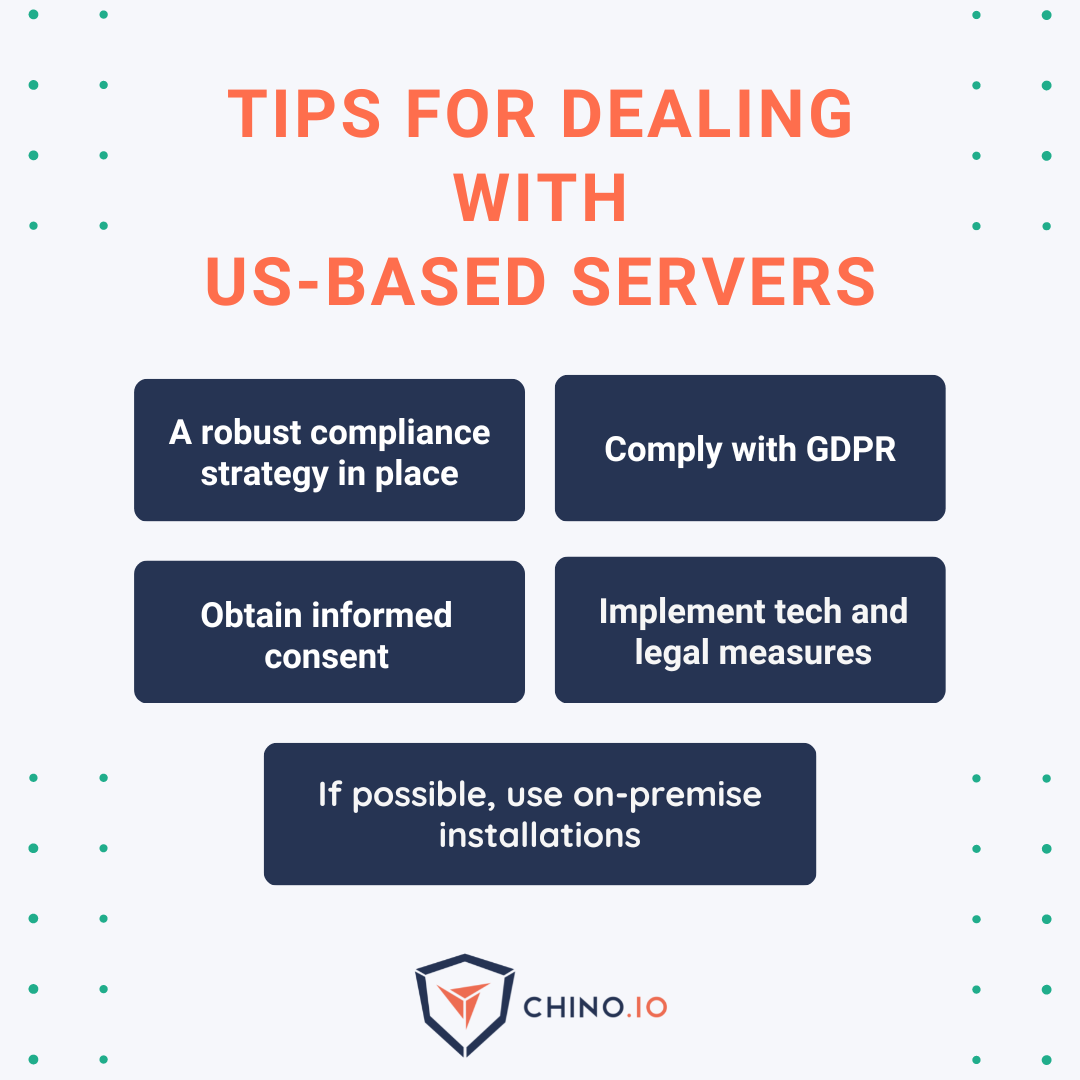
To summarise, this means that a GDPR compliant implementation of OpenAI would implement a series of organisational and technical measures to minimise data processing risks. Technical measures would include data partitioning / pseudonymisation, encryption, data minimisation, among others.
However, in the particular case of OpenAI, minimising these risks will be particularly tricky. Specially considering the next challenge:
Human Labelling and Training implications
ChatGPT, just like most of the language processing models out there, is trained using human labelling. This is a measure that is not only necessary to continue making the model useful, but also for reducing any biases and harmful answers that may arise.
How do the developers analyse the model outputs? Let’s see together the three main criteria:
- How much it can help: if the tool can follow the user’s instructions.
- How accurate is the output: if the trained model has tendencies for hallucinations on closed-domain tasks
- How harmful is the output: if the output is appropriate or contains biases or denigrations.
In order to assess this, it is not clear what information ChatGPT actually uses, which should be corroborated in the DPA.
This topic understandably generates great concerns with regards to the GDPR. In a recent interview, Guido Scorza, an Italian lawyer specialising in privacy and data protection and currently a member of the Board of the Authority for the Protection of Personal Data, declared:
"The chatbot stores - or, at least, can store - a global knowledge of hundreds of millions of people around the world, about their way of thinking, on the questions they ask themselves, their anxieties, fears, and worries.” (from the HuffPost, January 7, 2023).
It is not yet clear how to overcome this compliance challenge in particular, or how ChatGPT mitigates it. If the data is in clear in the US, or processed by OpenAI’s legal entity in any manner, then there will be big compliance risks that any company looking to leverage the tool will have to overcome.
[The EU is working on a regulation proposal for Artificial Intelligence that may impact every business dealing with it. If you are interested in reading more, click here!]
5 steps to start using ChatGPT (and ensure GDPR compliance)
With ChatGPT still in the training phase, it is essential to be careful and remember that privacy cannot be guaranteed.
For this reason, we suggest five simple steps to consider while using it:
- Start from the GDPR basics: be sure to have your GDPR compliance in place. The GDPR is always the starting point for all your data privacy and security actions, particularly a Record of Processing Activities.
- Get consent or any other legal basis if you want to use personal data on ChatGPT.
- Do not include any personal and sensitive data: Be careful of the information you are sharing with the tool. Avoid writing any personal information about your users if you don’t have consent, TIA, or DPAs.
- Always check the generated texts: focus on the output text generated by the tool and be aware of any personal information present.
- Delete in the platform any content that may contain personal information.
As seen before, being evaluated by a human part means that the data may include biases; thus, the generated text may not be immune from prejudice, discrimination, and racial implications. Thus, it is always essential to consult with a legal professional if you have specific questions or concerns about using ChatGPT or other AI technologies since this topic has broader implications.

What could make the adoption of chatGPT smoother for GDPR compliant companies?
What would be an ideal scenario for using ChatGPT in the EU and reducing privacy risks?
There are a few points that would make it safer and compliant with the current data privacy and protection laws. Let’s see some of them together:
- Running ChatGPT on-premise or in an EU-based cloud provider: running the service in a server based in the EU will avoid the great problem of US cloud providers, making it compliant with the GDPR.
- Implementation of (locally run) de-identification techniques to reduce amount and sensitivity of personal data shared
- Ability to limit what data is used for human review
Unfortunately, none of these features appear to be on the Professional Plan that the company is assessing to implement:
There is no doubt. This is a fantastic technology and a prime example of how quickly AI can reach the entire world.
After writing the article, we wanted to check how ready the platform is to replace us as the main authors. The results were very good - but we still hope you enjoyed our version better!

There are still a great number of legal issues and legal questions that could still stand in the way of widespread use. Against this rapid development, it seems sensible for the European Union to address such issues with the AI Act.
Taking the right precautions, ChatGPT will become a valuable tool in business, helping people benefit from Artificial Intelligence's advantages without significant privacy risks.
Chino.io, your trusted compliance partner
The one-stop shop for solving all privacy and security compliance aspects.
As a partner of our clients, we combine regulatory and technical expertise with a modular IT platform that allows digital applications to eliminate compliance risks and save costs and time.
Chino.io makes compliant-by-design innovation happen faster, combining legal know-how and data security technology for innovators.
To learn more, book a call with our experts.









